Digital Signatures: The Digital Equivalent of Signing a Paper
Salomon Kisters
Feb 12, 2021This post may contain affiliate links. If you use these links to buy something we may earn a commission. Thanks!
Ever since blockchain technology has started mapping real-world scenarios to a secure digital environment, we have observed an array of layman terms being repeated as well, for instance, the “digital signature”. In order to understand its significance and utility, it is important to understand what is your unique identifier in the real world – it happens to be your fingerprint, right?
Well, that’s exactly what is happening in the digital environment as well. Digital signatures are just like your fingerprints. So, in order to make it easy and understand in a better way, you can think of it as the digital equivalent of holding a pen and signing the paper or putting your thumb impression on an RFID.
How Do Digital Signatures Work?
Just to put everything straight, a digital signature basically works on a mathematical algorithm. Each time a document or file is being digitally signed, two keys are generated against it, called the public and private keys. Apart from that, a hash is also created for the entity that is signed to “seal” the contents of the file.
Once the hash is generated, it is encrypted with the private key of the signee and is stored in a “vault” and the entire “package” is forwarded to the recipient.
At the recipient side, your public key is used to verify that you have signed the document and approved the content inside it. Please note that the private key only belongs to you and will never be transmitted to the recipient or the mainstream open ledger. Only the public key is transmitted and that is also done to enable the recipient to decrypt the content of the file. Moreover, the recipient’s end of the network can also match the hash to ensure there has been no tampering with the content during transmission.
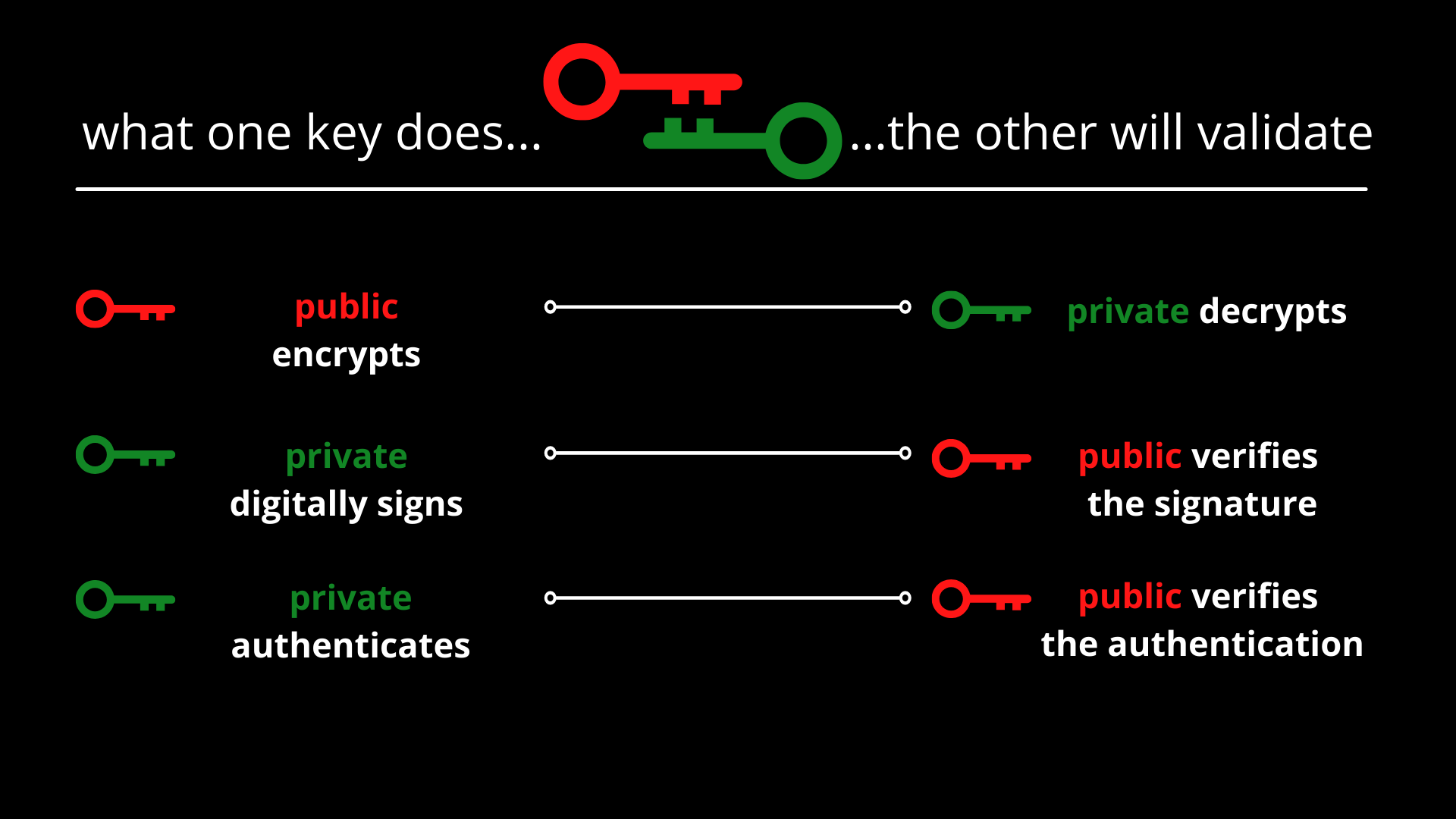
Public key vs. private key:
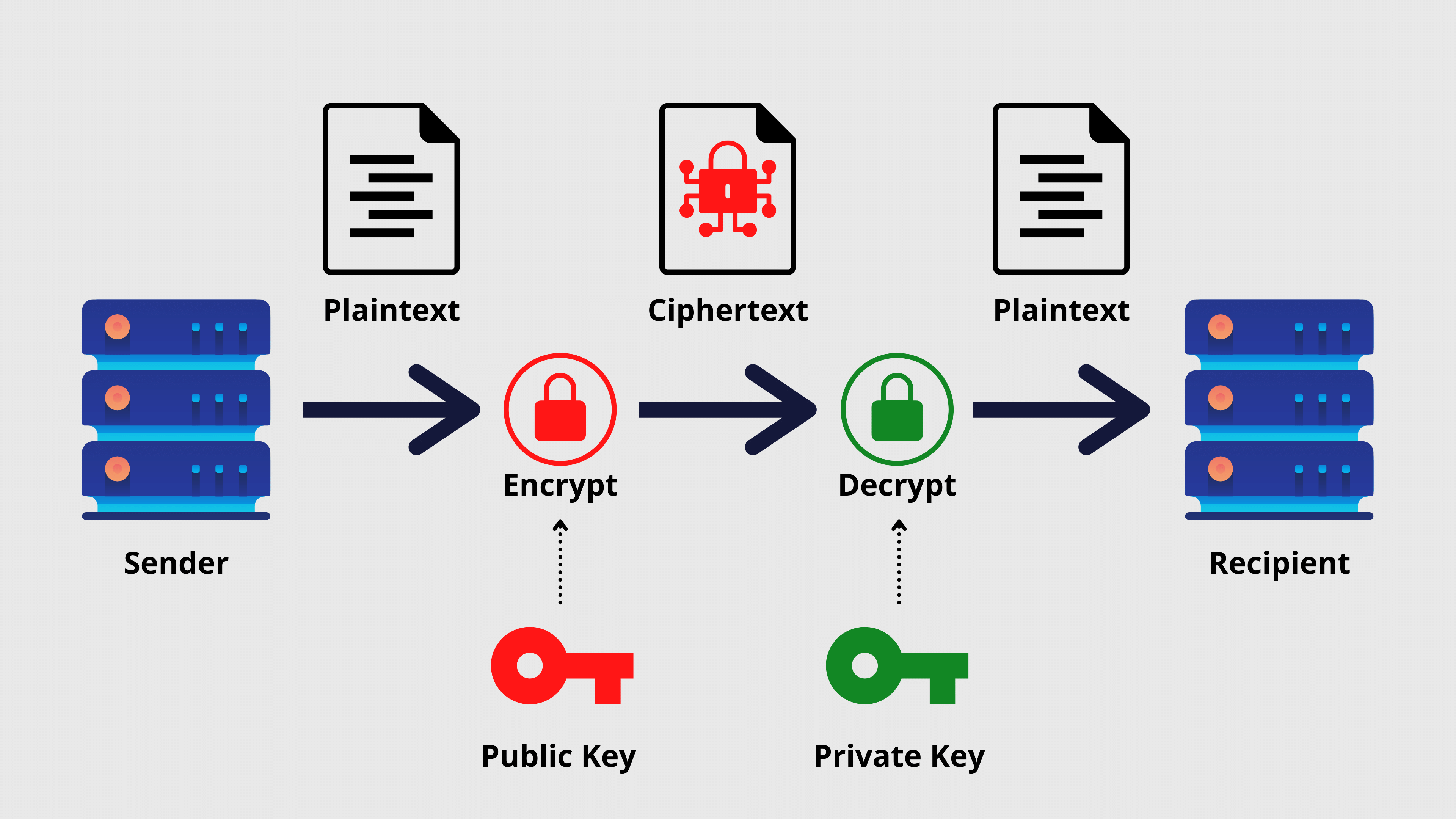 Here is a three-step process that defines the mechanism of digital signature:
Here is a three-step process that defines the mechanism of digital signature:
- Key generation algorithm: a private key is picked from the pre-defined pool randomly and the key is assigned to the entity being signed (e.g. a document). At this stage, after picking the private key, its public key is also decided. Please note that it’s kept random to ensure nobody can predict the behavior
- Signing algorithm: the system takes the private key and content as the input to generate a signature
- Verifying algorithm: it runs at the recipient’s end and takes the content/file, signature, and public key to ensure whether the content is authentic or has been tampered, based on the hash
It should be noted that the concept of signing the documents and files digitally has been around for decades, particularly in the legal and financial spheres. However, since the aspect of provenance is growing steadily after the popularity of blockchain technology, digital signatures have got a new dimension altogether.
If the digital signatures are implemented properly, like the way they are in most of the blockchain networks, they act as the perfect approach for non-repudiation, where nobody can deny their involvement. In this case, if John sends Michael a signed document, there is no way that anybody can refuse it or change the name of the sender.
The differences between public and private key is nicely described here.
At this point, it is worth mentioning that digital signatures should not be confused with electronic signatures, as the latter mentioned only relates to replicating your real-world signature (that you do on paper) and copying them on different documents. They have nothing to do with proving the ownership and creating the public and private keys. However, your digital signature may contain your electronic signature as a part of it only.
How Are They Different from Blockchain Timestamps?
Although these two terms are used quite extensively in the blockchain world, digital signatures and timestamps are often misinterpreted or rather interchanged by many.
To put it simply, a digital signature shows that a file or entity belongs to a specific person and the information inside the file is hashed. Therefore, the recipient or the viewer can be certain of the integrity of the file. On the contrary, blockchain timestamps simply hash the content of the file and allow the recipient to determine that the file existed at a particular time.
If you look at it carefully, in both types, the common element happens to be the timestamp which cannot be changed and is only issued when something is created or introduced to the network for the very first time. However, the “signature” in the entire digital signature process can be changed. For instance, if a file was created at a particular time, but is now owned by someone else, the signature will certainly change.
At OriginStamp, we use timestamping techniques to secure the Intellectual Properties in a single click. Therefore, if a creative person wants to timestamp his IP and protect any breach of copyright, he can simply upload it on our interface and generate a timestamp and hash against the file.
The Pros of Digital Signatures
Now that we have understood the concept and mainstream advantages behind digital signatures, let’s dive deeper and explore some of them (and others) in detail.

Extra Security
You must have realized it already in the above text where signatures and timestamps are compared heads-on.
Just to give you more insight about this, please note that once a “fingerprint-like” signature is embedded on a file, it cannot be removed from there, at all, unless the owner of the file (or any other digital entity) changes.
Since the PKI encryption technology is used, the digital signatures are the highest standard for identifying the person behind a signature.
Moreover, since the system takes the hash of the file, whenever a sign changes, the hash changes as well and the recipient can always tell if any part of the file has been tampered with.
Note: PKI defines an entire ecosystem that could consist of hardware, software, and even some procedures that are required to be executed in order to ensure that the digital signatures are managed in a secure environment and manner. Moreover, this protocol is also responsible for “forcing” the system to use other requirements for issuing digital signatures, such as a Certificate Authority, Enrollment Software, and Certificate Management.
Global Acceptance
The acceptance of blockchain technology was quite stunted initially. However, in the last 5-7 years, the urge to have decentralized and encrypted systems have grown exponentially. This is why governments across the World have also started accepting digital signatures into their legal framework.
As a result of this trend, platforms that provide that offer digital signing or timestamping capabilities, such as OriginStamp, are also becoming increasingly compliant with the relevant data protection laws in their respective jurisdictions. So, the overall trend of the industry and governments sounds very collaborative and the acceptance of digital signatures has also become mainstream.
Accessibility and Retention
Although an ordinary user needs to have access to a 3rd party to put the digital signature on a document, the role of the intermediary ends immediately when the record is pushed on the blockchain.
Since the published record contains your keys, signature, and the hash of the file, even if the 3rd party that you used goes out of business and ceases the operations, your files would still be traceable. This is mainly because of the decentralized nature of the blockchain technology that removes the single source of failure from the entire network.
Saves Time
Since the system is fully digital and decentralized as well, you as an end-user, do not have to wait for any relevant person to be in the office so you can sign something. It’s as simple as logging into your social media account and posting a tweet, without requiring anyone else, and the world knows who tweeted.
Moreover, since the entire process can be done at the press of a button, there is no need to go out of your house for signing the documents again.
So, the process is not only hassle-free for the end-users, but even the businesses can reduce their operational costs by moving everything into a digital environment and not having to pay anything to the unnecessary staff.
Business Efficiency
Since the intermediaries and manual processes are removed entirely, the embedding of signatures is also quite swift. As soon as the system takes the sign of the user, it can be saved to the system and can be applied to a variety of other pages (if required), without asking the user for his signature repeatedly.
Conclusion
Since organizations and agencies are drifting away from paperwork and Covid-19 has also fueled that transition, it is the perfect time to adopt digital measures, particularly the ones that are being executed in decentralized environments.
Apart from non-repudiation, there are several other reasons as well as to why this adoption is necessary, particularly for FinTech institutions. This is because the legitimacy of the sender needs to be established before an action is taken. For instance, if your bank sends a message to the central bank for depositing your account with $500, the central bank needs to determine and ensure that they have received the message from the verified source and only the entitled person is sending the message. Moreover, they also need to verify that the timestamp is intact to ensure when was the message dispatched and whether it still happens to be in an unaltered state or not.
Stay informed with the latest insights in Crypto, Blockchain, and Cyber-Security! Subscribe to our newsletter now to receive exclusive updates, expert analyses, and current developments directly to your inbox. Don't miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and stay up-to-date.
Love what you're reading? Subscribe for top stories in Crypto, Blockchain, and Cyber-Security. Stay informed with exclusive updates.
Please note that the Content may have been generated with the Help of AI. The editorial content of OriginStamp AG does not constitute a recommendation for investment or purchase advice. In principle, an investment can also lead to a total loss. Therefore, please seek advice before making an investment decision.

Top 6 Blockchain Books to Read in 2021 - Dive into Blockchain Technology
Discover the top 6 blockchain books to read in 2021 and delve into blockchain technology to understand its history, use cases, and future potential.

Using Blockchain Technology to Differentiate Your Business - A Competitive Advantage Guide
Learn how to leverage blockchain technology to gain a competitive advantage in your business. Explore examples and benefits of using blockchain for non-functional requirements.
Blockchain vs Database: Key Differences Explained
Understand the key differences between Blockchain and Database, from decentralization to security, in this detailed comparison.
Protect your documents
Your gateway to unforgeable data. Imprint the authenticity of your information with our blockchain timestamp